Modelling of a porous flowing electrolyte layer in a flowing electrolyte direct-methanol fuel cell
Duivesteyn, Eric, et al. “Modelling of a Porous Flowing Electrolyte
Layer in a Flowing Electrolyte Direct-Methanol Fuel Cell.”
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, vol. 38, no. 30,
8 Oct. 2013, pp. 13434—13442. Web of Science,
doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.08.017.
Presented by Juni Kim
Introduction (Direct Methanol Cell)
- Small Devices (e.g. golf carts, forklifts, electronic devices)
- Standard battery cell principles
- ABL → ACL (anode catalyst layer, oxidation occurs)
-
Redox Reaction separated by PEM (polymer electrolyte membrane,
protons pass through)
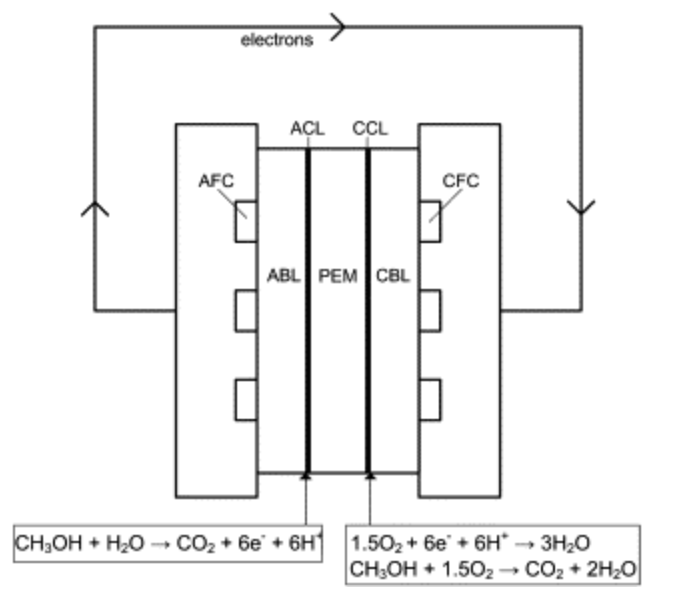
Introduction (Fluid Electrolyte-DMFC)
- Methanol Crossover- Methanol leaks through the PEM, reduces reaction efficiency
- Flowing Electrolyte Channel (H2SO4 sandwiched between PEM layers, washes away methanol)
- Porous Material as structural support + flow
- Ohmic losses b/c of the imperfect proton conductance of H2SO4
Introduction (Novelty)
- Typically modeled with a parabolic velocity profile (non-porous)
- Approach: include porous properties in modeling
Methods and Materials
Assumptions
- Constant Temperature, active area
- Water-like properties
- Laminar Flow
- Used PET (Polyethylene) spacer properties (porousness)
Results
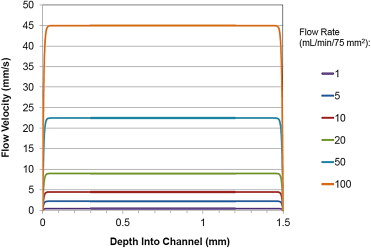
- Thin and constant boundary layer despite velocity flux
- Velocity Profile is relatively constant
Results (cont)
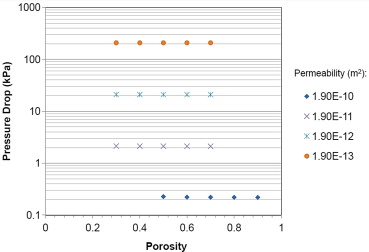
- Permeability (ability of H2SO4 to pass) - significant effects on pressure drop
- Porosity (amount of open space), relatively minimal effects
Conclusion
- Novelty in fluid flow modeling of a fluid electrolyte
- Maximize size of pores (permeability)
- Minimize size of channel (ohmic losses)
- Maximize Volume Flux (methanol crossover)
- Perhaps in research interest?
Modelling of a porous flowing electrolyte layer in a flowing
electrolyte direct-methanol fuel cell Duivesteyn, Eric, et al. “Modelling of a Porous Flowing Electrolyte
Layer in a Flowing Electrolyte Direct-Methanol Fuel Cell.” International Journal of Hydrogen Energy , vol. 38, no. 30,
8 Oct. 2013, pp. 13434—13442. Web of Science,
doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.08.017. Presented by Juni Kim